Disk2vhd v1.63
Disk2vhd is a utility that creates VHD (Virtual Hard Disk – Microsoft’s Virtual Machine disk format) versions of physical disks for use in Microsoft Virtual PC or Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machines (VMs). The difference between Disk2vhd and other physical-to-virtual tools is that you can run Disk2vhd on a system that’s online. Disk2vhd uses Windows’ Volume Snapshot capability, introduced in Windows XP, to create consistent point-in-time snapshots of the volumes you want to include in a conversion. You can even have Disk2vhd create the VHDs on local volumes, even ones being converted (though performance is better when the VHD is on a disk different than ones being converted).
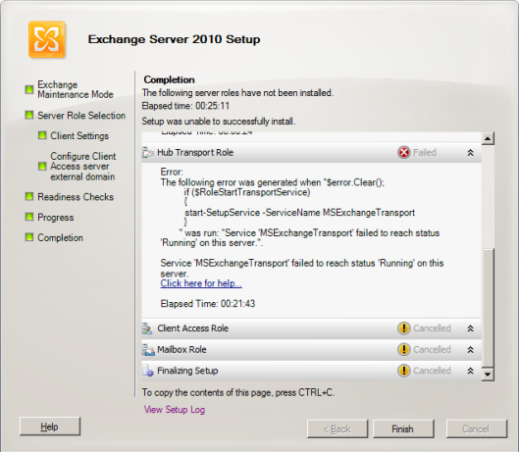
The Disk2vhd user interface lists the volumes present on the system:
.jpg)
It will create one VHD for each disk on which selected volumes reside. It preserves the partitioning information of the disk, but only copies the data contents for volumes on the disk that are selected. This enables you to capture just system volumes and exclude data volumes, for example.
Note: Virtual PC supports a maximum virtual disk size of 127GB. If you create a VHD from a larger disk it will not be accessible from a Virtual PC VM.
To use VHDs produced by Disk2vhd, create a VM with the desired characteristics and add the VHDs to the VM’s configuration as IDE disks. On first boot, a VM booting a captured copy of Windows will detect the VM’s hardware and automatically install drivers, if present in the image. If the required drivers are not present, install them via the Virtual PC or Hyper-V integration components. You can also attach to VHDs using the Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 Disk Management or Diskpart utilities.
Note: do not attach to VHDs on the same system on which you created them if you plan on booting from them. If you do so, Windows will assign the VHD a new disk signature to avoid a collision with the signature of the VHD’s source disk. Windows references disks in the boot configuration database (BCD) by disk signature, so when that happens Windows booted in a VM will fail to locate the boot disk.
Disk2vhd runs Windows XP SP2, Windows Server 2003 SP1, and higher, including x64 systems.
Here’s a screenshot of a copy of a Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V system running in a virtual machine on top of the system it was made from:
Command Line Usage
Disk2vhd includes command-line options that enable you to script the creation of VHDs. Specify the volumes you want included in a snapshot by drive letter (e.g. c:) or use “*” to include all volumes.
Usage: disk2vhd <[drive: [drive:]…]|[*]> <vhdfile> Example: disk2vhd * c:\vhd\snapshot.vhd
Note: Physical-to-virtual hard drive migration of a Windows installation is a valid function for customers with Software Assurance and full retail copies of Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7. Software Assurance provides users valuable benefits—please contact Microsoft Corporation for further information. Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7 installed by Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) using OEM versions of these products may not be transferred to a virtual hard drive in accordance with Microsoft licensing terms.
Download Disk2vhd (811 KB)
Run Disk2vhd now from Live.Sysinternals.com.
.png)